More Information about the Cytomegalovirus Antibody Test Kit
AccuQuik™ promotes the use of Cytomegalovirus Antibody Test Kit.
Cytomegalovirus Antibody
Available as strip or cassette
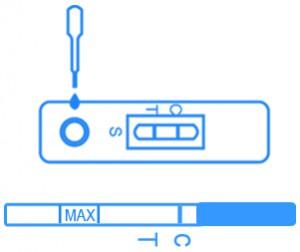
Cytomegalovirus Antibody Test Kit diagnostic test detects cytomegalovirus antibodies in the serum or plasma using an indirect fluorescent antibody assay. The test kit is comprised of two basic steps. First, specimen will react with the antigen substrate wherein they will bind to the antigen building antigen-antibody complexes if antibodies are present. In this step, complexes will not be formed without the presence of antibodies. Next, fluorescein-labeled anti-human IgG antibodies are added to the reacting site that binds with the antigen-antibody complex. A colored line will appear on the test kit as the complex is formed, indicating a positive result. No line will appear, indicating a negative result, if no complex is formed. AccuQuik™ promotes the use of Cytomegalovirus Antibody Test Kit.
The Disease
General Information
Cytomegalovirus is a common virus in the same family as herpesvirus that usually shows no symptoms or only mild illnesses. Due to its asymptomatic nature, infection of cytomegalovirus often went unnoticed. Mild symptoms that are similar to flu might occur for a few weeks and goes away while the virus remains in the body. However, individuals with compromised or weakened immune systems might activate the virus to cause serious illnesses such as hepatitis, colitis, pneumonia, retinitis or encephalitis. Individuals most at risk for serious complications are those with HIV/AIDS, organ/bone marrow transplant recipients, and chemotherapy patients. A pregnant woman can pass infection to the developing baby, causing physical and developmental problems to the baby, such as hearing/vision problems, pneumonia, seizures and delayed mental development.
Treatments
While there is no specific cure for cytomegalovirus infection, treatments can be provided on case-by-case basis. Healthy adults generally do not need any specific treatment for the infection. In people with immunocompromised conditions such as individuals with AIDS, treatments are usually administered to correct the underlying immune disorders by appropriate medical prescriptions. Other individuals who are susceptible to serious illnesses due to the infection, such as organ transplant recipients, may need treatment to suppress the building infection. The treatment for babies infected will depend on the type of symptoms, as well as its severity. Prevention against cytomegalovirus infection is most important in pregnant women, frequent hand washing and not sharing food, drinks or utensils with other children can also reduce risk of infection as the virus is spread from direct contact of body fluids.