More Information about the Fecal Occult Blood Test Kit
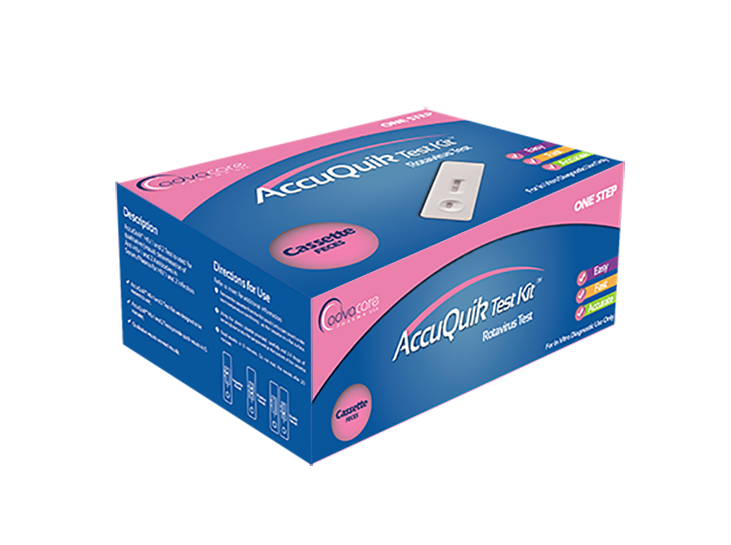
AccuQuik™ promotes the use of Fecal Occult Blood Test Kit.
Fecal Occult Blood
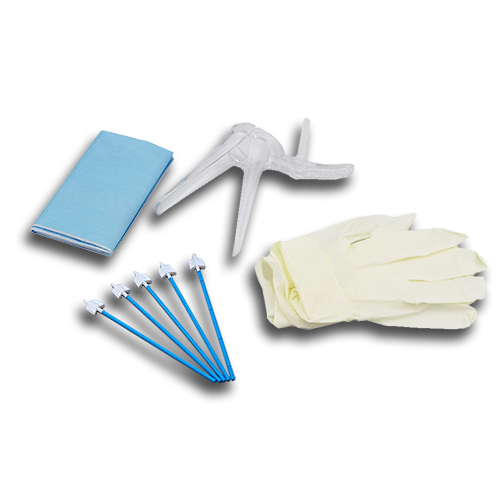
Available as strip or cassette
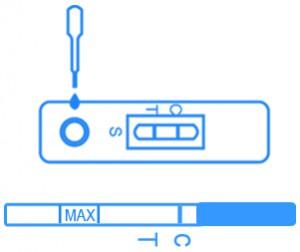
Fecal Occult Blood Test Kit diagnostic test detects human occult blood in feces using a chromatographic immunoassay qualitative detection. In the test kit, anti-hemoglobin antibodies are pre-coated on the membrane on the test line of the test. When specimen is added, it will react with the anti-hemoglobin antibody. The created mixture moves upward by capillary action on the membrane chromatographically. In the case of a positive result, the mixture reacts with the anti-hemoglobin antibody on the membrane chromatographically and creating a colored line. If no colored line is formed, the results of the test are negative. A Control line is present to indicate whether or not enough volume of specimen has been used. AccuQuik™ promotes the use of Fecal Occult Blood Test Kit.
The Disease
General Information
Fecal occult blood usually occurs when there is slow bleeding from the inside of the lower or gastrointestinal tract. In the case of slow bleeding, the color of feces does not change to a reddish color that usually indicates blood. Thus, a fecal occult blood test is required to detect the presence of bleeding or not. Many diseases may be asymptomatic or with non-visible symptoms, and can only be detected with fecal occult blood test. Some these diseases are colon cancer, ulcers, polyps, colitis, diverticulitis, and fissures. It is most commonly used for colon cancer screening when a gastrointestinal bleeding is suspected. During the early stages of the disease, symptoms are rarely visible. Symptoms in the later stages may include abdominal pain, rectal bleeding or changes in bowel habits (diarrhea or constipation).
Treatments
Treatments for colon cancer might vary depending on the size or location of the cancer, or your other health concerns. Surgery to remove the cancer is often administered both for early and advanced-stage colon cancer. Chemotherapy or radiation therapy might also be recommended. Prevention or early detection is highly recommended by doctors. As risk of the disease increases with older age, doctors recommended a yearly testing of colon cancer at age 50. Lifestyle changes may be implemented in the long-term to reduce risk of colon cancer, including: including a diet that is rich in fiber, vitamins, minerals and antioxidants, limiting the amount of alcohol consumption, quit smoking, staying active or exercising regularly, and maintaining a healthy weight.