More Information about the Chlamydia Test Kit
AccuQuik™ promotes the use of Chlamydia Test Kit.
Chlamydia Test Kit
Available as strip or cassette
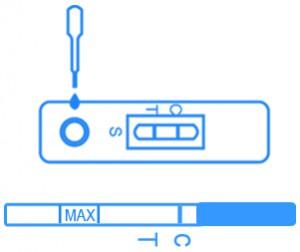
Chlamydia Test Kit diagnostic test detects Chlamydia trachomatis antigen qualitatively and rapidly. The test kit detects Chlamydia Trachomatis antigens present in specimen that could be obtained by female endocervical swab or male penile swab and male urine specimens. The test kit contains polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies. One antibody is on a porous membrane and the other antibody dye particles signal the test results. Chlamydia trachomatis antigen is present when the dying antibody binds with it and creates and antigen-antibody complex. It is a one-step take with 99% accuracy that delivers quick interpretable results in 10 minutes. The sensitivity and specificity of the test are fully validated and fulfill the basic requirements of rapid diagnostic tests.
AccuQuik™ promotes the use of Chlamydia Test Kit.
The Disease
General Information
Chlamydia trachomatis is a species of bacterial pathogens that causes one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases in humans. Chlamydia is most commonly found in sexually active individuals such as younger people between the ages 15-24. Around two-thirds of newly infected Chlamydia cases are in the age group. Chlamydia can be transmitted through anal, vaginal, or oral sex, or from mother to a baby during childbirth. The disease often shows no symptoms while remains transmissible. Over 25% of men and 70% of women with chlamydia have no symptoms. In symptomatic cases, common symptoms appear after one to three weeks of getting infected. These symptoms can be painful periods, bleeding between periods, abdominal pain and fever, pain during intercourse, itching, and also pain when urinating.
Treatments
Once a patient is diagnosed with Chlamydia, it is recommended to abstain from sexual intercourse until infection is eradicated. The cure rate of the disease is 95% but due to the asymptomatic nature of the disease, most women do not know they have the disease until serious complications arise. Oral antibiotics are prescribed as treatment, usually taken for 7 to 14 days. Antibiotics should be taken until the prescription is finished, even when symptoms have already receded. It is recommended for the patient’s partner(s) to also get treatment to prevent reinfection. Women with more serious infections, such as pelvic inflammatory disease, might need further treatment. Usually, a longer course of antibiotics might be prescribed or hospitalization might be required to administer intravenous antibiotics or surgery.