More Information about the Typhoid IgG/IgM Test Kit
AccuQuik™ promotes the use of Typhoid IgG/IgM Test Kit.
Typhoid IgG/IgM
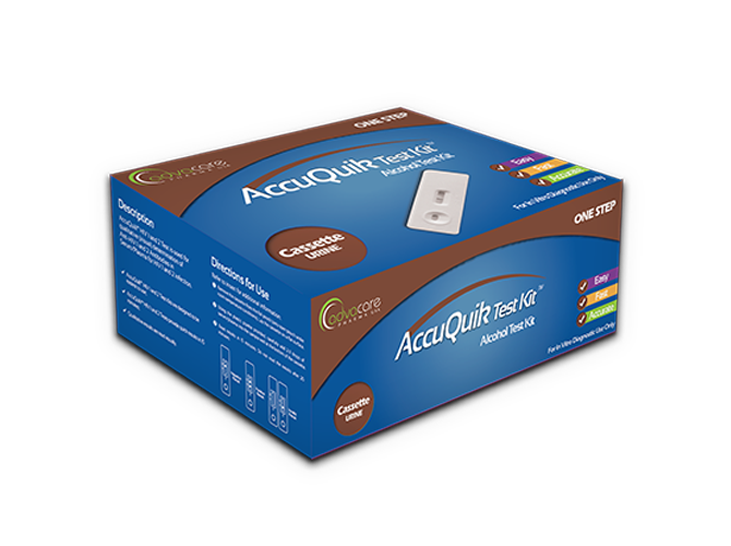
Available as cassette
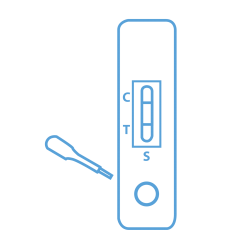
Typhoid IgG/IgM Test Kit diagnostic test detects and differentiates the IgG and IgM antibodies against the pathogenic bacteria Salmonella typhi (S. Typhi) using rapid immunoassay in whole blood or serum. The test kit is used as a screening test and aid in the diagnosis of infection with S. Typhi (typhoid). The typhoid IgG/IgM test kit is consisting of two components, an IgG component that is pre-coated with reagents for the detection of anti-S. Typhi IgG, and an IgM component that is pre-coated with monoclonal anti-human IgM for the detection of anti-S Typhi IgM. When the specific antibodies are present, a colored line will appear in the test zone, indicating a positive result. When the pathogen-specific IgM antibodies are not present, no line will appear in the test zone, indicating a negative result. AccuQuik™ promotes the use of Typhoid IgG/IgM Test Kit.
The Disease
General Information
Typhoid fever is a life-threatening illness caused by the infection of Salmonella Typhi bacteria. The infection of the bacteria could lead to high fever, diarrhea, and vomiting. The symptoms are often accompanied by weakness, abdominal pain, constipation, headaches, and mild vomiting. Without treatment, the symptoms may last for months, with increasingly dangerous complications such as: intestinal hemorrhage, intestinal perforation, encephalitis, pneumonia or acute bronchitis, neuropsychiatric symptoms, metastatic abscesses, and low platelet count. Typhoid is spread by eating or drinking contaminated food or water and usually occurs in areas with poor sanitation and poor hygiene. Children and young adults are at the highest risk of being infected, and the risk of death may be as high as 20% without treatment.
Treatments
With the availability of antibiotics and treatment, the risk of death for typhoid could drop to 1%. Antibiotics are the most effective way of treatment for typhoid. However, a recent surge in antibiotic resistance could be a problem. To ease symptoms and reduce the risk of deaths from dehydration and diarrhea, oral rehydration therapy can be administered. Surgery is necessary when intestinal perforation occurs. Usually, a simple closure of the perforation with drainage of the peritoneum is preferred. Prevention is important to control the outbreaks of typhoid, prevention measures include: frequent handwashing especially during food preparation, avoiding drinking untreated water, and providing properly sanitized environment. Vaccine for typhoid is available, however, they are not 100% effective and require repeat immunizations.